INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT)
1:Devices & Sensors – Physical objects like smart home appliances, wearables, industrial machines, and medical devices that collect data. 2:Connectivity – IoT devices use communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, Zigbee, or LoRaWAN to transmit data.
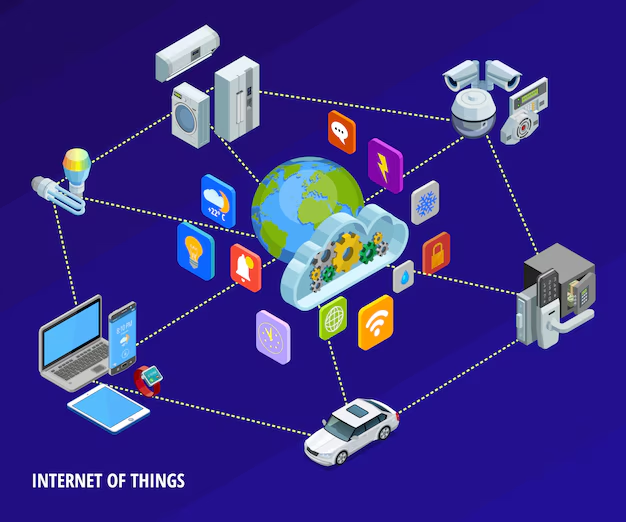
Cloud Computing – Data collected by IoT devices is stored and processed in cloud platforms like AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Google Cloud IoT. Edge Computing – Processing data closer to the source (device) to reduce latency and improve efficiency.

AI & Machine Learning – AI analyzes IoT data for insights, automation, and predictive maintenance. Security & Privacy – Protecting IoT devices from cyber threats through encryption, authentication, and firewalls.

✔ Smart Homes – Smart thermostats, lights, and security systems (e.g., Google Nest, Amazon Echo). ✔ Healthcare – Wearable health monitors, remote patient monitoring, and smart medical devices. ✔ Industrial IoT (IIoT) – Factory automation, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization. ✔ Smart Cities – Traffic monitoring, waste management, and energy-efficient lighting. ✔ Agriculture – Smart irrigation, soil monitoring, and livestock tracking. ✔ Retail – Smart inventory management, cashier-less stores (e.g., Amazon Go). ✔ Automotive – Connected cars, self-driving vehicles, and fleet management.

